2.2.7.2. How to respond to availability zone (AZ) failures¶
This chapter explains how to respond to a failure in the availability zone (AZ) of a mijin Catapult(v.2) VPC on AWS.
- creation-day:
Aug. 1, 2022
- update date:
September 14, 2022
2.2.7.2.1. mijin Catapult(v.2) Product Edition Configuration¶
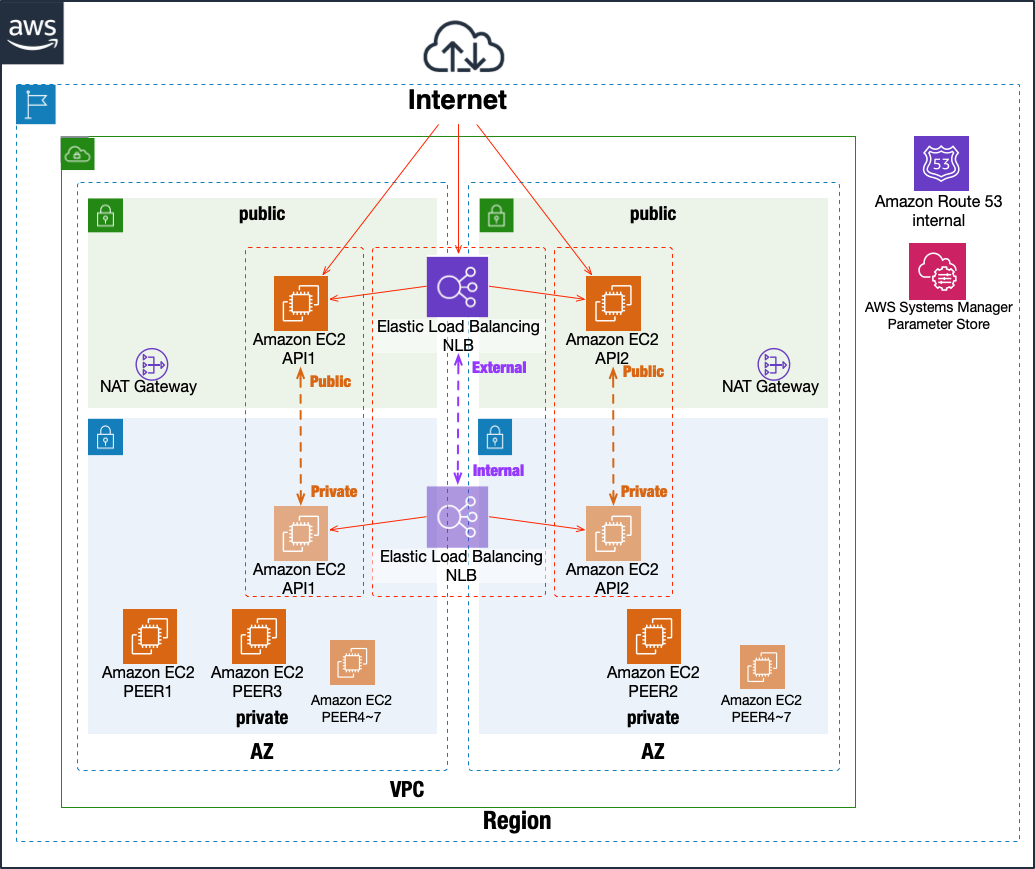
mijin Catapult(v.2) In the production version, the VPC is located in one region and the nodes are distributed across two availability zones (AZs).
By enabling ELB installation in the deployment parameters, service can continue even if one of the AZs fails.
mijin Catapult(v.2) can update blockchain data with a single PEER node.
If you want to access it from a program, etc., a single API node is all you need to continue accessing it.
For example, even if the entire service surrounded by the left AZ stops, as shown in the figure below, mijin Catapult(v.2) will not stop.
2.2.7.2.2. How to respond after AZ restoration¶
After AZ restoration, the response is simple.
mijin Catapult(v.2) automatically connects to the node with the running blockchain data after recovery (after the EC2 instance is started) and starts synchronizing the data.
Therefore, no special work is required for restoration.
To check if a node is restored, you can check by command or browser as follows.
http://{mijin endpoint}:3000/node/peers
$ curl http://mijinエンドポイント:3000/node/peers
[
{
"version": 0,
"publicKey": "9073B0A623934996A9AAAC85C6DEC8540AE17258D6997E42E00100CCFE6848EF",
"networkGenerationHashSeed": "B319300B02B12264B7DF867F0EFD583CC3C6E65ED2732E3FD77BBC1DE8E00E85",
"roles": 70,
"port": 7900,
"networkIdentifier": 96,
"host": "api1.mijin.internal",
"friendlyName": "api1.mijin.internal"
},
{
"version": 0,
"publicKey": "82DA8AE358AC7DF7BC97103A6ABE0F791A1655E20633CC387ACE198A0B7E9AA0",
"networkGenerationHashSeed": "B319300B02B12264B7DF867F0EFD583CC3C6E65ED2732E3FD77BBC1DE8E00E85",
"roles": 69,
"port": 7900,
"networkIdentifier": 96,
"host": "peer2.mijin.internal",
"friendlyName": "peer2.mijin.internal"
},
{
"version": 0,
"publicKey": "4EE257A9DD6D3F19331A467C6C76BA86B50B1297181E32C7A83C1184B666996C",
"networkGenerationHashSeed": "B319300B02B12264B7DF867F0EFD583CC3C6E65ED2732E3FD77BBC1DE8E00E85",
"roles": 69,
"port": 7900,
"networkIdentifier": 96,
"host": "peer1.mijin.internal",
"friendlyName": "peer1.mijin.internal"
},
{
"version": 0,
"publicKey": "C158D513266B2C04216CDC03AD99036757A41AD2AFDF59D2A67F6D2D4F8CC84F",
"networkGenerationHashSeed": "B319300B02B12264B7DF867F0EFD583CC3C6E65ED2732E3FD77BBC1DE8E00E85",
"roles": 69,
"port": 7900,
"networkIdentifier": 96,
"host": "peer3.mijin.internal",
"friendlyName": "peer3.mijin.internal"
}
]
If a node cannot be confirmed above, the blockchain data may be corrupted by a sudden node.
In that case, the mijin Catapult(v.2) node resynchronization or Restore from a backed-up snapshot to recover the node.
